Rotator Cuff Patch Augmentation
Overview
Rotator Cuff Repair with Augmentation, also known as Rotator Cuff Patch Augmentation, is a surgical procedure designed to enhance the healing and strength of torn rotator cuff tendons that have not responded to conservative treatments. This procedure involves the placement of a bio-inductive collagen implant over the tear. The implant, derived from purified bovine tendon, stimulates the body’s natural healing process, encouraging new tissue growth and reinforcing the tendon without the need for a full repair. Patients typically experience a quicker recovery and significant pain relief compared to traditional rotator cuff repair surgeries.
Anatomy
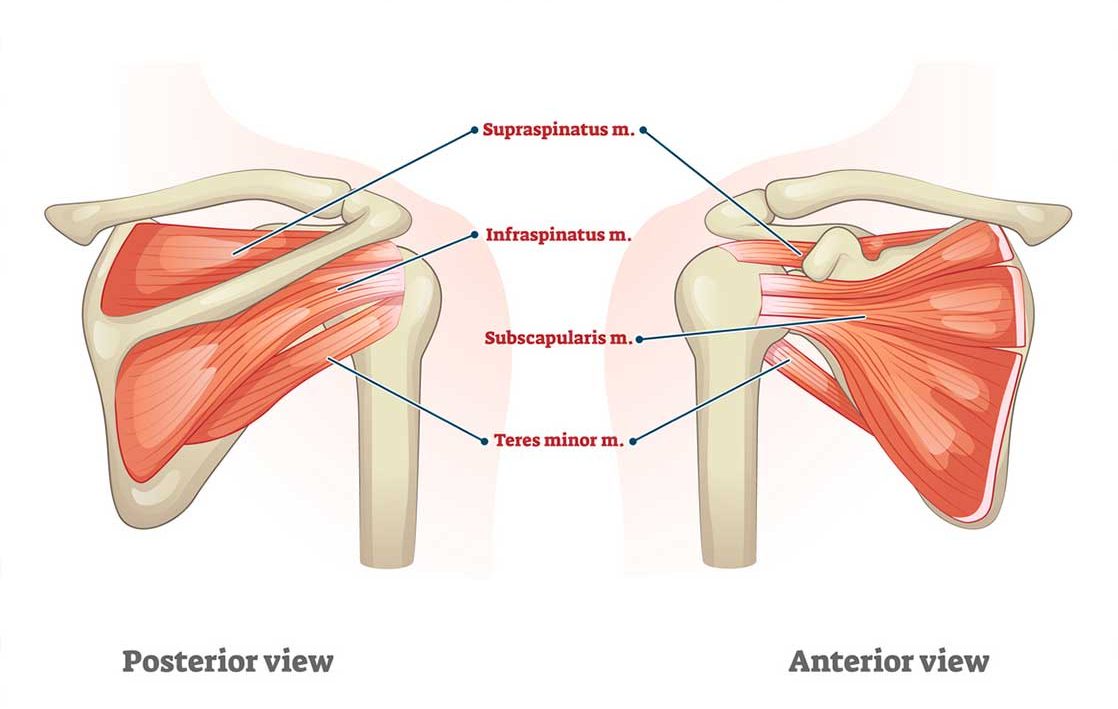
The rotator cuff is a group of four muscles—supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis—that stabilise the shoulder joint and enable a wide range of arm movements. These muscles, along with their tendons, attach to the bones of the shoulder, including the humerus, scapula, and clavicle. In rotator cuff injuries, these tendons can become torn or frayed, leading to pain, weakness, and restricted mobility. The Rotator Cuff Augmentation procedure targets these tendons, promoting healing and reinforcing the strength of the rotator cuff.
What is Rotator Cuff Repair with Augmentation?
Rotator Cuff Repair with Augmentation is typically performed arthroscopically, meaning it is minimally invasive and involves small incisions and a camera to guide the surgery. During the procedure, a bio-inductive collagen implant, such as the Regeneten™ Bioinductive Implant, is placed over the site of the rotator cuff tear. This implant, made from highly purified bovine tendon, encourages the body’s natural healing response by stimulating new tendon growth. The implant is absorbed by the body over time, and in most cases, tendon thickness increases, leading to improved function and reduced pain.
In some cases, Rotator Cuff Graft Augmentation can be used to augment a full rotator cuff repair or in revision surgeries where previous repairs have not fully healed. The implant can also be inserted during partial tear repairs, allowing patients to resume normal activities more quickly, as the recovery time is typically shorter compared to a full rotator cuff repair.

Rotator Cuff Graft Augmentation Techniques
Rotator Cuff Graft Augmentation can be performed in various scenarios depending on the extent of the tear and the patient’s condition. Here are the main types:
- Partial Tear Augmentation: Used when there is a partial thickness tear in the rotator cuff that is symptomatic but does not require a full repair. The bio-inductive patch is placed over the tear to promote healing and strengthen the tendon.
- Full Repair Augmentation: In cases where a full rotator cuff repair is necessary, the patch can be used in conjunction with the repair to reinforce the tendon and improve healing outcomes.
- Revision Repair Augmentation: This type is used in patients who have previously undergone rotator cuff repair but did not achieve full healing. The patch may help to stimulate additional tendon growth and repair the previously damaged area.
Conditions That May Require This Surgery
Rotator Cuff Graft Augmentation is indicated for specific conditions where conservative treatments have failed. These include:
- Partial Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears: When the tear involves only a portion of the tendon and causes significant pain or weakness, patch augmentation can be an effective treatment.
- Failed Previous Rotator Cuff Repairs: If a previous rotator cuff surgery did not fully heal, augmentation with a patch can help restore tendon function and reduce pain.
- Recurrent Rotator Cuff Tears: Patients with repeated rotator cuff injuries may benefit from patch augmentation to strengthen the tendon and prevent further damage.
Benefits and Risks
The primary benefits of Rotator Cuff Graft Augmentation include quicker recovery time, reduced pain, and improved tendon strength. The minimally invasive nature of the procedure also means less scarring and a shorter rehabilitation period compared to traditional rotator cuff repairs.
However, like any surgery, there are risks involved. These may include infection, implant rejection, or incomplete healing of the tendon. Additionally, not all rotator cuff tears are suitable for patch augmentation, and the success of the procedure depends on factors such as the size and location of the tear, as well as the patient’s overall health.
What Should I Expect?
- Before the Procedure: Mr. Soong Chua will conduct a thorough assessment of your shoulder, including imaging studies like MRI or ultrasound, to determine the extent of the tear and whether graft augmentation is appropriate. You will be advised on pre-operative care, which may include ceasing certain medications and arranging for post-operative support at home.
- During the Procedure: The surgery is performed arthroscopically, usually under general anaesthesia. Small incisions are made around the shoulder, and the collagen patch is positioned over the tear. If a full repair is necessary, this will be done simultaneously. The procedure typically takes 1-2 hours.
- After the Procedure: You will likely need to wear a sling for about 6 weeks to protect the shoulder while it heals. Physiotherapy will be essential in regaining strength and mobility. Most patients can expect to resume normal activities within 3-6 months, though full recovery may take longer.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How long does the bio-inductive implant last?
The bio-inductive implant is absorbed by the body within approximately 6 months. During this time, it promotes the growth of new tendon tissue, which increases the thickness and strength of the rotator cuff. - Is the surgery painful?
Post-operative pain is common but can be managed with medications and proper care. The pain typically decreases as the tendon heals and rehabilitation progresses. - Will I need physiotherapy after the surgery?
Yes, physiotherapy is crucial for a successful recovery. Your physiotherapist will guide you through exercises to restore strength and flexibility to the shoulder, tailored to your individual recovery process. - How soon can I return to work after the surgery?
The timeline for returning to work varies depending on the nature of your job and the extent of your surgery. Office-based workers may return to light duties within a few weeks, while those with physically demanding jobs might need several months before resuming full duties.

