Robotic Knee Replacement Melbourne
Overview
Knee replacement surgery is a transformative procedure designed to alleviate pain and restore function in individuals suffering from severe knee conditions. Dr Soong Chua specialises in both traditional and advanced robotic knee replacement surgery in Melbourne, ensuring the highest precision and patient satisfaction.
Anatomy
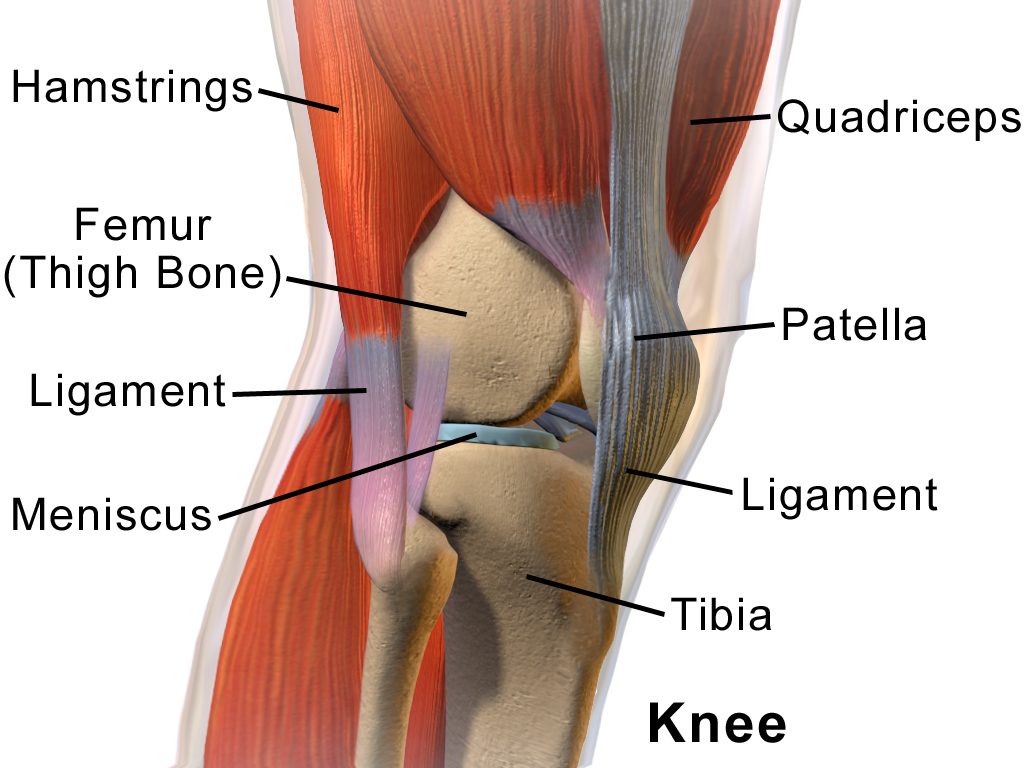
The knee is a complex hinge joint composed of bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons. The major components include:
- Femur (thigh bone)
- Tibia (shin bone)
- Patella (kneecap)
- Cartilage: Cushions the ends of the bones and allows smooth movement.
- Ligaments: Connect bones and provide stability.
- Tendons: Connect muscles to bones.
These components work together to provide the knee with stability, flexibility, and strength, enabling a wide range of movements essential for daily activities.
What is Knee Replacement Surgery?
A knee replacement, or knee arthroplasty, involves removing damaged parts of the knee joint and replacing them with artificial components, known as implants. This procedure aims to replicate the function of a healthy knee joint, relieving pain and improving mobility.
Types of Knee Replacement Procedures
1. Traditional Knee Replacements
Traditionally, knee replacements have been implanted with manual alignment, where the surgeon tries to match the normal alignment of the knee using jigs and guides placed by hand. This has been and still is a reliable and safe surgical procedure but malalignment can occur. Surgeons have continually strived to achieve better accuracy and alignment. This led to the development and use of computer navigation.
2. Robotic Knee Replacements
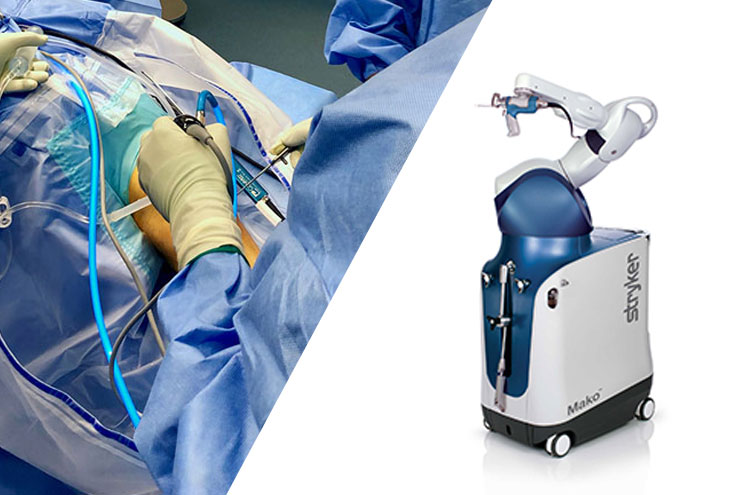
Robotic knee replacement surgery enhances precision by using advanced computer navigation and robotic systems. This approach reduces the risk of malalignment and ensures a more accurate fit of the implant, leading to better outcomes for patients.
With robotic assistance, Dr Chua and his team are able to achieve greater accuracy leading to improved alignment and enhanced function of the knee replacement. He is also able to tailor the surgery to the patient’s anatomy, minimising tissue damage which leads to less scarring and quicker healing.
- The Mako Robotic Arm
The Mako robotic arm system allows for pre-surgical planning and real-time adjustments during the procedure. A preoperative CT scan generates a 3D model of the patient’s knee, which guides the surgery with unparalleled accuracy.In the preoperative planning stage, a detailed 3D model of the knee is created from a CT scan. Dr Soong Chua uses this model to plan the optimal implant position and alignment tailored to the patient’s anatomy. The surgery can be simulated to anticipate any issues and make necessary adjustments.Dr Chua still performs the surgery, using the robot arm to make cuts for implanting the knee replacement. The system provides real-time feedback, allowing for adjustments during the procedure to ensure perfect alignment. The robotic arm ensures that all movements are within predefined safe limits, protecting surrounding tissues.
Conditions That May Require Knee Replacement Surgery
Knee replacement surgery is typically recommended for patients with:
- Osteoarthritis: A degenerative joint disease, causing cartilage breakdown.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune condition leading to joint inflammation.
- Post-Traumatic Arthritis: Arthritis resulting from a knee injury.
- Severe knee fractures: That cannot be effectively treated with other methods.
Benefits and Risks
Knee replacement surgery offers several significant advantages for patients suffering from debilitating knee pain and limited mobility. The following are some of the key benefits that this procedure can provide:
- Significant Pain Relief: Knee replacement surgery effectively alleviates chronic pain from conditions like osteoarthritis or severe injury, enabling patients to enjoy a more comfortable and active lifestyle.
- Improved Mobility and Knee Function: Patients typically notice a substantial improvement in knee movement and stability, allowing them to walk, climb stairs, and participate in physical activities with greater ease.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: With reduced pain and improved mobility, patients can return to their favourite activities and perform daily tasks more comfortably, leading to better overall mental and emotional well-being.
As with any surgical procedure, there are certain risks associated with knee replacement surgery. It’s important for patients to be aware of these potential complications before undergoing the operation. Common risks include:
- Anaesthetic risks
- Infection
- Blood clots
- Implant loosening or wear over time
- Stiffness
- Fractures
- Nerve or blood vessel damage
Frequently Asked Questions
- How long does a knee replacement surgery typically last?
The duration of knee replacement surgery varies depending on factors such as the patient’s overall health, the complexity of the procedure, and the surgical approach used. On average, knee replacement surgery usually takes between one to two hours. Robotic knee replacement surgery initially took slightly longer however with experience and honing of techniques, Dr Chua now performs robotic surgery in less time than traditional knee replacement. Dr Chua will provide you with more specific information tailored to your individual case during your consultation. - How long is the recovery period after a knee replacement?
Recovery typically takes 6-12 weeks, with ongoing improvement for up to a year. Physical therapy is crucial for a successful recovery. - Is robotic knee replacement better than traditional methods?
Robotic knee replacement offers greater accuracy and personalisation, which can lead to better outcomes and faster recovery times compared to traditional methods; however, a traditional knee replacement is still a reliable option in cases where robotic surgery is not possible. - Can any surgeon perform a robotic knee replacement?
No. Robotic knee replacements can only be performed by certain surgeons and knee replacement specialists who have completed strict training requirements and are accredited to use the Mako robot. Mr Chua was one of the first surgeons to be accredited to use the Mako robot for knee replacements in Melbourne. He has since furthered his skills on surgical visits to the United States.Only certain hospitals in which the operating theatre staff have undergone specific training will gain accreditation to use the Mako robot.Mr Chua is able to perform this procedure at the Epworth Private Hospital in Richmond as well as the Epworth Eastern in Box Hill, as they have all been accredited for Mako robotic surgery.